Table of Contents
ToggleDeciding Between the New and Old Tax Regime for FY 2023-2024 (AY 2024-2025)
As the financial year 2023-2024 (assessment year 2024-2025) approaches, taxpayers are faced with a significant decision: whether to opt for the new tax regime introduced by the government or stick with the old tax regime. This decision can have a substantial impact on your tax liability and financial planning for the upcoming year. In this blog post, we’ll explore the key differences between the two tax regimes and guide to help you make an informed choice.

Accepting the New Tax Regime:
The new tax regime, introduced in the Union Budget of 2020, aims to simplify the tax structure and offer taxpayers the flexibility to choose between a lower tax rate without deductions or a higher tax rate with deductions. Under this regime, taxpayers have the option to forgo claiming various deductions and exemptions available under the old tax regime in exchange for lower tax rates.
Key Features of the New Tax Regime
To understand the impact of the new tax regime on your finances, let’s take a closer look at the tax rates applicable for FY 2023-2024 (AY 2024-2025) under both regimes:

Comparing Tax Liabilities:
Let’s compare the tax liabilities under both tax regimes for different income levels using examples:
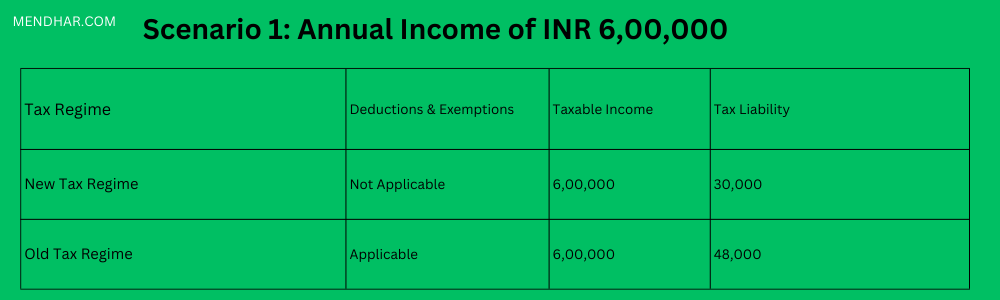
In this scenario, opting for the new tax regime results in a lower tax liability of INR 30,000 compared to INR 48,000 under the old tax regime.
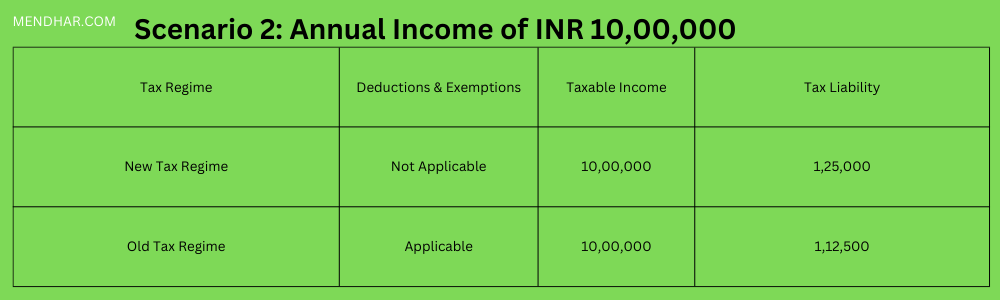
In this scenario, opting for the old tax regime results in a slightly lower tax liability of INR 1,12,500 compared to INR 1,25,000 under the new tax regime.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Tax Regime:
Income Level: Your annual income plays a crucial role in determining which tax regime is more beneficial for you. Analyze your income and tax liability under both regimes to make an informed decision.
Deductions and Exemptions: Consider the deductions and exemptions available under the old tax regime and assess whether you can maximize tax savings by claiming them.
Simplicity vs. Tax Savings: The new tax regime offers simplicity with lower tax rates but sacrifices deductions and exemptions. Evaluate whether the convenience of a lower tax rate outweighs the potential tax savings from deductions and exemptions.

Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Financial Future
When deciding which tax regime to use for FY 2023–2024 (AY 2024–2025), you should carefully analyze your income, available deductions, and desired tax savings. You may make an educated choice that supports your long-term financial goals by weighing the tax obligations under the two regimes and evaluating your unique financial circumstances. Never forget to seek the advice of a financial counselor or tax specialist for individualized advice based on your unique situation and demands.
FAQs for Income Tax Slabs for Financial Year 2023-2024
1. What are Income Tax Slabs for FY 2023-2024?
- For individuals below 60 years of age:
- Up to ₹2.5 lakh: Nil
- ₹2,50,001 to ₹5 lakh: 5%
- ₹5,00,001 to ₹10 lakh: 20%
- Above ₹10 lakh: 30%
- For individuals aged 60 years or above but below 80 years (Senior Citizens):
- Up to ₹3 lakh: Nil
- ₹3,00,001 to ₹5 lakh: 5%
- ₹5,00,001 to ₹10 lakh: 20%
- Above ₹10 lakh: 30%
- For individuals aged 80 years or above (Super Senior Citizens):
- Up to ₹5 lakh: Nil
- ₹5,00,001 to ₹10 lakh: 20%
- Above ₹10 lakh: 30%
2. Are there any additional surcharges or cess applicable?
- Yes, a surcharge is applicable if the total income exceeds certain limits:
- For individuals having a total income exceeding ₹50 lakh but not exceeding ₹1 crore: 10% of income tax
- For individuals having a total income exceeding ₹1 crore but not exceeding ₹2 crore: 15% of income tax
- For individuals having a total income exceeding ₹2 crore but not exceeding ₹5 crore: 25% of income tax
- For individuals having a total income exceeding ₹5 crore: 37% of income tax
- Health and Education Cess: 4% of income tax including surcharge, if applicable.
3. What are the deductions available under various sections?
- Deductions under Section 80C, 80CCC, and 80CCD (1) combined up to ₹1.5 lakh.
- Deduction for interest paid on housing loan (Section 24) up to ₹2 lakh.
- Deduction for interest paid on education loan (Section 80E) for the entire interest amount.
- Deduction for medical insurance premium (Section 80D) up to ₹25,000 (₹50,000 for senior citizens).
- Deduction for donations to specified entities (Section 80G) subject to specified limits.
4. Are there any exemptions for specific incomes?
- Agricultural income is exempt from income tax.
- Certain allowances such as HRA (House Rent Allowance), LTA (Leave Travel Allowance), etc., are exempt up to specified limits and conditions.
5. How can I file my income tax return?
- Income tax returns can be filed online on the Income Tax Department’s e-filing portal or through authorized intermediaries.
- Alternatively, physical filing can be done by submitting the filled-in forms at designated income tax offices.
6. What is the due date for filing income tax returns for FY 2023-2024?
- The due date typically falls on July 31 of the assessment year. However, it’s advisable to check the current year’s due date as it may vary based on government notifications.
7. What happens if I miss the deadline for filing returns?
- Late filing can attract penalties and interest on the tax payable.
- It may also lead to loss of certain benefits such as carry-forward of losses or deduction claims.
8. Can I revise my income tax return if I make a mistake?
- Yes, you can file a revised return within a specified time frame if you discover any errors or omissions in your original return.
9. Are there any specific documents I need to keep for income tax purposes?
- It’s important to maintain documents such as Form 16 (TDS certificate), bank statements, investment proofs, rent receipts, etc., to support your income, deductions, and exemptions claimed in your return.
10. Where can I find more information or assistance regarding income tax matters?
- You can refer to the official website of the Income Tax Department for detailed information, or consult with a tax advisor for personalized assistance.


Pingback: Important Dates of ITR Filing FY 2023-24 (AY 2024-25) -
Pingback: 4% Hike In DA For Central Government Employees -
Pingback: How to Record Students Co-curricular Activities -