Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Intimation Under Section 143 of the Income Tax Act

Intimation under Section 143 of the Income Tax Act is a crucial aspect of the tax assessment process in India. This section deals with the preliminary assessment of tax returns filed by taxpayers. The term “intimation under Section 143” refers to the initial communication sent by the Income Tax Department to the taxpayer, indicating the status of their tax return after a basic verification process. This intimation can either be an acknowledgment of the return filed, an adjustment of the tax amount, or a notice requiring further information.
The primary purpose of intimation under Section 143 is to verify the correctness of the tax return filed by the taxpayer. This process ensures that the details provided in the return are accurate and in compliance with the provisions of the Income Tax Act. It is essential for taxpayers to understand the significance of this intimation and respond appropriately if required. Failure to comply with the requirements of the intimation can lead to penalties and further scrutiny by the Income Tax Department.
The Process of Intimation Under Section 143:
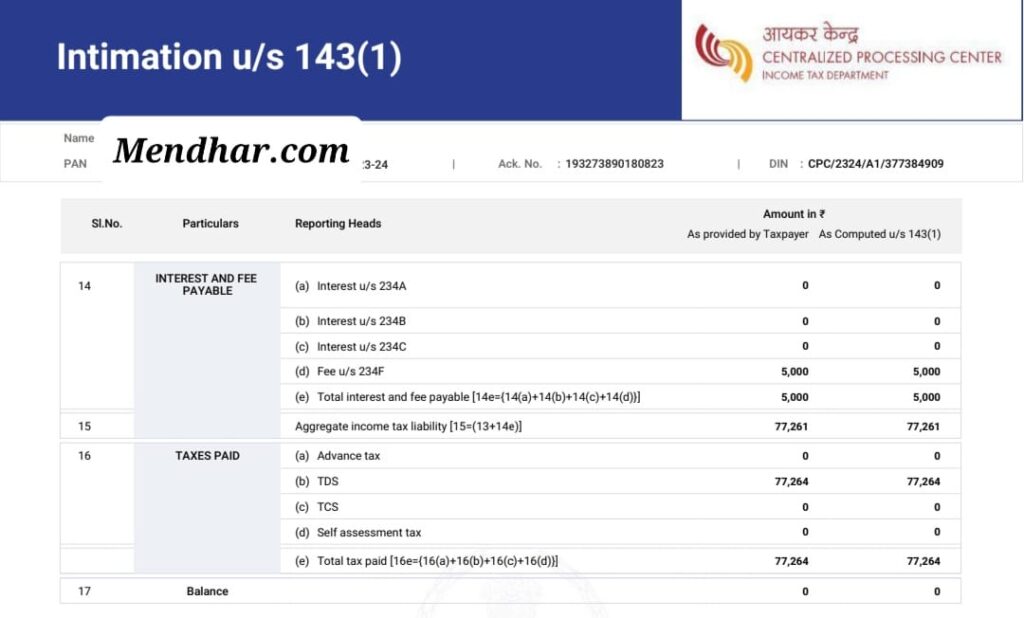
The process of intimation under Section 143 begins with the filing of the income tax return by the taxpayer. Once the return is filed, the Income Tax Department processes it through a computerized system to check for any discrepancies or errors. If the system finds no discrepancies, an intimation under Section 143(1) is issued. This intimation serves as an acknowledgment of the return filed and indicates that the return has been accepted as it is.
However, if the system detects discrepancies, adjustments are made to the return, and the intimation under Section 143(1) will reflect these changes. The adjustments may include arithmetical errors, incorrect claims, or inconsistencies between the return and the details available with the department. The taxpayer is then informed about these adjustments through the intimation. It is important to note that the taxpayer has the right to respond to the intimation and provide explanations or corrections if they believe the adjustments are incorrect.
Types of Intimation Under Section 143:
Intimation under Section 143 can be classified into two types: intimation under Section 143(1) and notice under Section 143(2).
Intimation under Section 143(1) is a preliminary assessment and does not involve any detailed scrutiny of the return. It is issued within a period of one year from the end of the financial year in which the return is filed. This intimation can result in three scenarios: no demand or refund, a demand for additional tax, or a refund due to the taxpayer. If there is no demand or refund, the intimation serves as a confirmation that the return has been accepted. If there is a demand for additional tax, the taxpayer must pay the amount specified in the intimation. If a refund is due, the department will process it accordingly.
Notice under Section 143(2), on the other hand, is issued if the department decides to scrutinize the return in detail. This notice is issued within six months from the end of the financial year in which the return is filed. The purpose of this notice is to ensure that the taxpayer has not understated their income, claimed excessive deductions, or paid less tax than required. The taxpayer is required to provide additional information and documents to support the claims made in the return. Failure to respond to this notice can result in penalties and further action by the department.
Responding to Intimation Under Section 143:
It is crucial for taxpayers to respond promptly and accurately to intimation under Section 143. If the intimation under Section 143(1) indicates no discrepancies or a refund, the taxpayer need not take any further action. However, if the intimation reflects adjustments or a demand for additional tax, the taxpayer should carefully review the details and respond accordingly.
If the taxpayer agrees with the adjustments made by the department, they should pay the additional tax within the specified time frame to avoid penalties. Payment can be made online through the Income Tax Department’s website or at designated banks. If the taxpayer disagrees with the adjustments, they can file a rectification request under Section 154 of the Income Tax Act. This request should include detailed explanations and supporting documents to justify the corrections. The department will review the request and issue a revised intimation if necessary.
Importance of Keeping Records:
Maintaining accurate and comprehensive records is vital for addressing intimation under Section 143 effectively. Taxpayers should keep copies of all documents related to their income, deductions, investments, and other relevant financial transactions. These records will be essential if there is a need to respond to an intimation or a notice under Section 143.
Additionally, taxpayers should regularly check their registered email and the Income Tax Department’s e-filing portal for any communications or notices. Prompt attention to these communications can prevent unnecessary complications and ensure timely compliance with the department’s requirements.
Conclusion:
Intimation under Section 143 of the Income Tax Act plays a significant role in the tax assessment process in India. Understanding the implications of this intimation and responding appropriately is essential for taxpayers to ensure compliance with tax laws and avoid penalties. By maintaining accurate records, promptly reviewing intimations, and taking necessary actions, taxpayers can navigate the tax assessment process smoothly and efficiently. The importance of being vigilant and proactive in dealing with intimation under Section 143 cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the taxpayer’s financial standing and compliance status.
In conclusion, intimation under Section 143 serves as a preliminary assessment tool used by the Income Tax Department to verify the accuracy of tax returns. Taxpayers should be well-informed about the types of intimation, the process involved, and the appropriate steps to take in response. By doing so, they can ensure that their tax returns are accurate, compliant, and free from discrepancies, ultimately contributing to a transparent and efficient tax system.