Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding EVM: A Modern Solution to Secure Voting
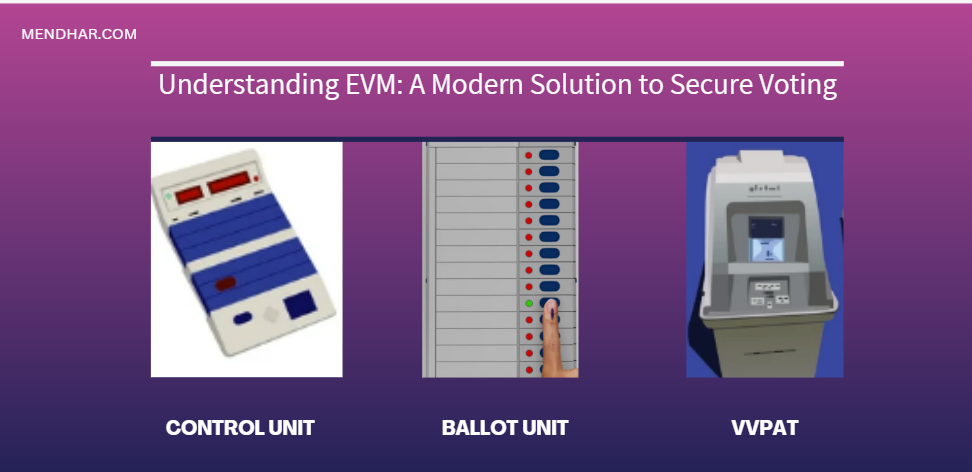
In the realm of modern democracy, the Electronic Voting Machine, commonly known as EVM, stands as a beacon of technological advancement in the electoral process. As societies evolve, so do their methods of voting. Gone are the days of paper ballots and cumbersome manual counting; EVMs have revolutionized the way we cast our votes, making elections more efficient, accurate, and secure.
What is EVM?
EVM, or Electronic Voting Machine, is a device used to facilitate electronic voting in elections. It’s a sleek, compact machine that simplifies the voting process by allowing voters to cast their ballots electronically.
How Does EVM Work?
EVMs work by presenting voters with a list of candidates and political parties on a digital display. Voters then select their preferred candidate by pressing a button or touching a screen. Once the vote is cast, the machine records it electronically. At the end of the voting period, the EVM tallies up all the votes automatically, providing quick and accurate results.
Benefits of EVM:
Accuracy: EVMs eliminate the possibility of errors in vote counting, ensuring that every vote is recorded and counted accurately.
Efficiency: With EVMs, the voting process is much faster compared to traditional paper ballots, reducing long queues and waiting times at polling stations.
Security: EVMs are designed with multiple layers of security to prevent tampering and ensure the integrity of the electoral process.
Cost-Effective: While the initial investment in EVM technology may be significant, it ultimately saves money in the long run by reducing the need for manual labor in counting and recounting votes.
History of EVM:
The concept of electronic voting dates back to the late 19th century, but it wasn’t until the late 20th century that EVMs began to gain widespread use. The first electronic voting machines were introduced in the United States in the 1960s, but it wasn’t until the early 2000s that they became widely adopted.
Controversies Surrounding EVMs:
Despite their many benefits, EVMs have not been without controversy. Some critics argue that electronic voting machines are susceptible to hacking and tampering, potentially compromising the integrity of election results. However, proponents of EVMs argue that they are equipped with robust security features to prevent such tampering.
EVMs Around the World:
EVMs are used in countries around the world, from India to Brazil to the United States. Each country may have its own specific model of EVM tailored to its unique electoral needs, but the basic principles of electronic voting remain the same.
Future of EVMs:
As technology continues to advance, so too will the capabilities of EVMs. Future iterations of electronic voting machines may incorporate biometric authentication, blockchain technology, and other innovations to further enhance security and transparency in the electoral process.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, EVMs represent a significant leap forward in the evolution of democracy. By streamlining the voting process, improving accuracy, and enhancing security, electronic voting machines have become an essential tool in ensuring free and fair elections around the world. While they may not be without their challenges, the benefits of EVMs far outweigh the drawbacks, making them a cornerstone of modern electoral systems.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs)
1. What is an EVM?
An Electronic Voting Machine (EVM) is a device used for electronic voting in elections. It allows voters to cast their ballots electronically, simplifying the voting process and automating the counting of votes.
2. How does an EVM work?
EVMs present voters with a list of candidates and political parties on a digital display. Voters select their preferred candidate by pressing a button or touching a screen. The machine then records the vote electronically and tallies up all the votes at the end of the voting period.
3. Are EVMs secure?
EVMs are designed with multiple layers of security to prevent tampering and ensure the integrity of the electoral process. They incorporate features such as encryption, secure hardware, and strict access controls to safeguard against hacking and manipulation.
4. Can EVMs be hacked?
While no system is completely immune to hacking, EVMs are equipped with robust security measures to minimize the risk of tampering. Additionally, strict protocols are in place to monitor and audit the use of EVMs during elections to detect any irregularities.
5. What are the benefits of using EVMs?
- Accuracy: EVMs eliminate the possibility of errors in vote counting, ensuring that every vote is recorded and counted accurately.
- Efficiency: EVMs streamline the voting process, reducing long queues and waiting times at polling stations.
- Security: EVMs incorporate multiple security features to prevent tampering and safeguard the integrity of elections.
- Cost-effectiveness: While there may be an initial investment in EVM technology, it ultimately saves money by reducing the need for manual labor in counting and recounting votes.
6. Are EVMs used worldwide?
Yes, EVMs are used in countries around the world, including India, Brazil, the United States, and many others. Each country may have its own specific model of EVM tailored to its unique electoral needs.
7. What are some controversies surrounding EVMs?
Despite their benefits, EVMs have faced criticism from some quarters. Concerns have been raised about their susceptibility to hacking and tampering, as well as the lack of transparency in the software used in EVMs. However, proponents argue that EVMs are equipped with robust security measures to address these concerns.
8. What does the future hold for EVMs?
As technology continues to advance, EVMs are likely to evolve to incorporate new innovations such as biometric authentication and blockchain technology. These advancements will further enhance the security and transparency of the electoral process, ensuring free and fair elections for all.


Pingback: Essential Tips for Handling and Operating an EVM: A Comprehensive Guide -